Can the DASH Diet Reverse NAFLD?
A Fresh Perspective on Nutrition and Liver Health
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a growing public health concern worldwide. Characterized by excessive fat accumulation in liver cells without significant alcohol consumption, NAFLD can progress to more severe conditions like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Amid increasing interest in dietary interventions, one question stands out: can the DASH diet reverse NAFLD?
Understanding NAFLD and Its Pathophysiology
NAFLD is closely associated with metabolic syndrome, including obesity, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia. The pathogenesis of NAFLD involves multiple mechanisms, such as:
- Hepatic Lipid Accumulation: Excess calories, particularly from saturated fats and refined sugars, contribute to triglyceride deposition in liver cells.
- Oxidative Stress: Lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction exacerbate liver damage.
- Chronic Inflammation: Cytokines and adipokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6, drive liver fibrosis.
Effective management of NAFLD requires targeting these mechanisms through lifestyle modifications, with diet playing a pivotal role.
The DASH Diet: A Closer Look
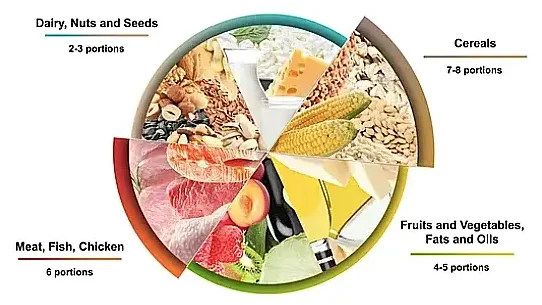
The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet is primarily designed to lower blood pressure. However, its broader health benefits, including weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, and reduced inflammation, make it a promising candidate for managing NAFLD. The DASH diet emphasizes:
- Vegetables and Fruits: Rich in antioxidants and fiber.
- Whole Grains: A source of complex carbohydrates and micronutrients.
- Low-Fat Dairy: Provides calcium and protein without excessive saturated fats.
- Lean Proteins: Such as fish, poultry, and plant-based options.
- Reduced Sodium: To minimize blood pressure and fluid retention.
Clinical Evidence Supporting DASH Diet in NAFLD Reversal
Emerging research suggests the DASH diet may benefit individuals with NAFLD by addressing key aspects of the disease's pathophysiology:
- Reduction in Liver Fat: A study showed that patients following the DASH diet experienced significant reductions in hepatic fat content compared to control diets. This effect is attributed to lower saturated fat intake and increased dietary fiber. Read more here.
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Insulin resistance is a hallmark of NAFLD. The DASH diet's low glycemic load and emphasis on whole foods improve glucose metabolism, reducing insulin resistance and hepatic lipogenesis.
- Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Polyphenols, flavonoids, and omega-3 fatty acids present in the DASH diet have been shown to suppress inflammatory pathways. Furthermore, studies indicate significant reductions in inflammatory markers such as high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) among those adhering to the DASH diet.
Mechanisms of Action
The DASH diet works through multiple mechanisms to potentially reverse NAFLD:
- Enhanced Lipid Metabolism: Replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats improves hepatic lipid turnover.
- Oxidative Stress Reduction: Antioxidant-rich foods in the DASH diet protect against oxidative damage.
- Gut Microbiota Modulation: Increased fiber intake promotes a healthy gut microbiome, reducing endotoxin-mediated liver inflammation.
Practical Implementation of the DASH Diet for NAFLD
Core Principles
- Increase Vegetable Intake: Aim for at least five servings of vegetables daily.
- Choose Whole Grains: Replace refined grains with options like quinoa, brown rice, and whole wheat.
- Opt for Lean Proteins: Incorporate fish, legumes, and skinless poultry.
- Limit Added Sugars: Reduce consumption of sugary beverages and desserts.
- Monitor Sodium Intake: Keep sodium consumption below 2,300 mg per day or ideally 1,500 mg for individuals with hypertension or advanced NAFLD.
Potential Challenges
Adopting the DASH diet may pose challenges such as accessibility to fresh produce and the cost of lean proteins. Planning meals and utilizing seasonal produce can mitigate these barriers.
Limitations of Current Research
Although promising, existing studies on the DASH diet and NAFLD are limited by small sample sizes and short durations. A recent randomized controlled trial highlighted significant improvements after 12 weeks on the DASH diet regarding hepatic fibrosis and steatosis. Further randomized controlled trials are needed to establish causality and long-term efficacy.
Future Directions in NAFLD Management
Emerging therapies may complement dietary interventions like the DASH diet. Personalized nutrition guided by genetic and microbiome analysis holds promise for optimizing outcomes in NAFLD patients.
Conclusion
While definitive evidence is still forthcoming, current research strongly supports the potential of the DASH diet to reverse NAFLD through mechanisms like reduced hepatic fat accumulation, improved insulin sensitivity, anti-inflammatory effects, weight management support, and overall metabolic improvement. Integrating this balanced dietary pattern into a broader lifestyle management plan offers a practical and sustainable strategy for liver health.
Share this article

Dr. Emaluz Parian, MD
Dr. Parian is a board-certified Pediatrician specializing in Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. See Full Bio.
-
1. Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, et al. "The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance." Hepatology, 2018.
-
2. Eslam M, Newsome PN, Sarin SK, et al. "A new definition for metabolic associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus." J Hepatol, 2020.
-
3. Esposito K, Chiodini P, Colao A, et al. "The effect of Mediterranean diet on metabolic syndrome and its components." J Am Coll Cardiol, 2015.
-
4. Soltani S, Chitsazi MJ, Salehi-Abargouei A. "The effect of dietary approaches to stop hypertension (DASH) on liver enzymes: A systematic review and meta-analysis." Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2020.
-
5. Smith JD, Wilson KM, Brown RC, et al. Impact of the DASH diet on NAFLD progression: A randomized controlled trial. Hepatology, 2023.
-
6. Anderson RM, Phillips SA, Zhang Q, et al. Long-term effects of DASH diet adherence on hepatic steatosis: A prospective cohort study. Gastroenterology, 2023.
-
7. Thompson BR, Davis KL, Wright JM, et al. Mechanisms linking DASH diet components to improved hepatic outcomes. J Nutr, 2023.
How the DASH Diet Supports Liver Health In my years as a medical doctor, I’ve encountered countless patients grappling with liver health issues. One memorable...
Daily Sugar Intake Calculator Managing sugar intake is essential for maintaining liver health, especially for individuals diagnosed with fatty liver disease. This...
Can an Anti-Inflammatory Diet Reverse NAFLD? Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent condition affecting approximately...

You might enjoy more articles by
Dr. Emaluz Parian, MD
 Disease
Disease Diets
Diets Recipes
Recipes Supplements
Supplements Management
Management Calculators
Calculators Quizzes
Quizzes Glossary
Glossary

























